Sports nutrition and overall wellness have brought essential amino acids into the spotlight. These small organic compounds are the building blocks of proteins, and without them, no repair, growth, or energy production processes in the body would be possible. Among the most important, isoleucine plays a key role, especially when seeking physical performance, sustained energy, and better recovery after exercise. And the most interesting thing is that it's not only found in supplements or protein powders: nature provides it in everyday and delicious foods like nuts.
Today we'll see why isoleucine is so important, what its role is in the body, and how nuts become a true superfood that provides this essential amino acid.
What is isoleucine and why is it essential?
Isoleucine is one of the nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot synthesize on its own, meaning that it must be obtained through food.
It belongs to the group of branched-chain amino acids, or BCAAs (along with leucine and valine). These three amino acids have been extensively studied in sports and nutritional contexts, as they promote muscle repair and energy supply during physical activity.
The role of isoleucine includes:
- Participate in muscle protein synthesis.
- Contribute to the regulation of blood sugar levels.
- Stimulate energy production at the cellular level.
- Facilitate muscle recovery after intense training.
- Supporting a healthy immune system.
Without this amino acid, physical endurance and the repair of muscle fibers would be much less efficient.
Isoleucine and energy: the athlete's internal engine
When the body is under maximum demand—whether during a gym session, a half-marathon, or strength training—isoleucine plays a key role as a source of energy. Unlike other amino acids that are metabolized only in the liver, BCAAs like isoleucine can be oxidized directly in muscle tissue during exertion.
This means that when glycogen stores begin to decline, isoleucine kicks in, providing fuel to the muscles and delaying fatigue. This effect can translate into:
- Increased endurance during prolonged training sessions.
- Decreased feeling of exhaustion.
- Less muscle fiber breakdown during exertion.
Therefore, it is considered an essential amino acid in the diet of athletes and active people.
Muscle recovery and tissue regeneration
After each workout, muscles experience micro-tears in their fibers. The body needs to repair these tiny tears, and to do so, it requires an adequate supply of amino acids. Isoleucine plays a role here as a promoter of protein synthesis, helping to rebuild tissue and supporting balanced muscle growth.
Besides:
- It helps maintain nitrogen balance in the body, which is key to an anabolic state.
- It stimulates faster recovery after intense training.
- It reduces muscle pain associated with repetitive effort.
In combination with the other BCAAs, isoleucine acts as a true repair agent that accelerates the return to normal after training.
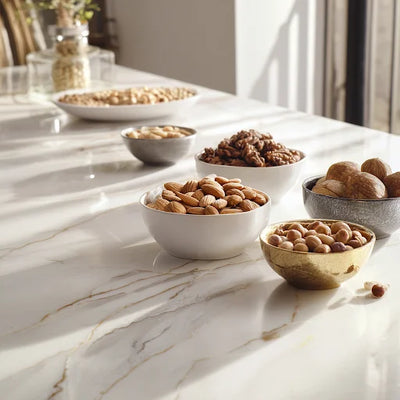
Nuts: the natural source of isoleucine
Although many people think BCAAs are only found in supplements, nature offers a range of foods that contain them in high proportions. Among these, nuts stand out, as they are not only rich in healthy fats, protein, and minerals, but also in isoleucine.
Nuts provide this amino acid in a balanced way that is easily integrated into the daily diet. Some examples:
-
Almonds : Almonds contain approximately 0.75 grams of isoleucine per 100 grams, although defatted versions or almond flour can contain up to 1.8 grams due to their higher protein content. They are also rich in vegetable protein, calcium, and vitamin E, providing a good amount of isoleucine per serving.
-
Walnuts : In addition to their content of plant-based omega-3 fatty acids, they contain significant levels of this amino acid. In the case of common walnuts, the value ranges from 0.62 to 0.96 grams depending on the source and variety.
-
Hazelnuts : Hazelnuts contain approximately 0.55 grams of isoleucine per 100 grams, according to comparative food amino acid sources.
-
Cashews : Cashews and cashew nuts also stand out, with values close to 0.8 grams per 100 grams. Perfect for those seeking energy, they combine healthy carbohydrates with protein, including isoleucine.
-
Pistachios : considered one of the most complete nuts, they provide protein, fiber, and essential amino acids. Although their overall profile is slightly lower, they still contribute significant amounts for muscle and energy recovery.
Thanks to this nutritional richness, nuts become ideal allies for those who want to boost energy and muscle recovery without relying solely on supplements.
How to incorporate more isoleucine through nuts
The best way to reap the benefits of isoleucine is to consume nuts regularly as part of a balanced diet. Some practical ideas:
- Add almonds or walnuts to natural yogurt for a quick snack.
- Include pistachios or cashews in salads to add texture and plant-based protein.
- Prepare a homemade mix of nuts to take to the gym or to work.
- Use nut butter as a topping on oatmeal or energy smoothies.
A daily serving of 25-30 grams of nuts not only contributes to isoleucine intake, but also improves metabolic and cardiovascular health.
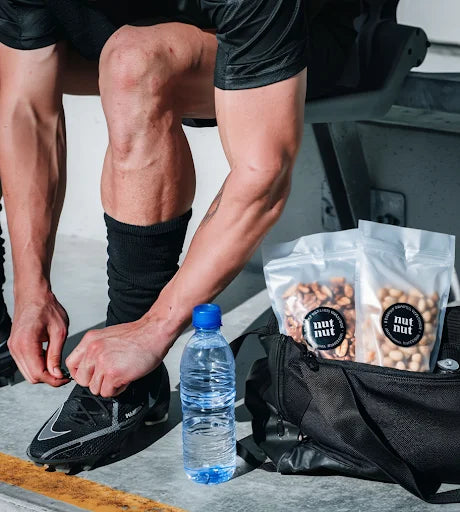
Add isoleucine to your body through nuts to improve your athletic performance.
Want to boost your training, performance, and recovery in a delicious and natural way? Nuts are the answer: a convenient and rich source of isoleucine, energy, and well-being in every bite.





Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.