Tocopherol, commonly known as vitamin E, is a fat-soluble nutrient essential for the human body. Its main function is as an antioxidant, protecting cell membranes from damage caused by free radicals, which is key to preventing premature aging and various chronic diseases.
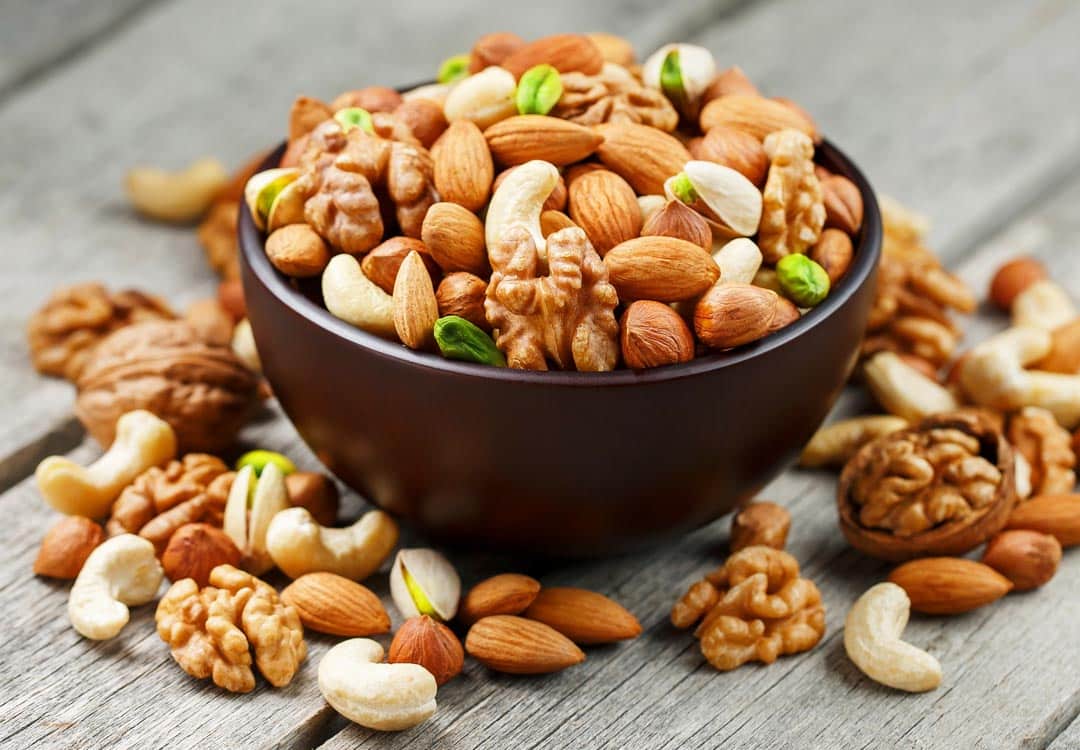
Nuts: natural source of tocopherol
Nuts stand out among the richest sources of vitamin E in the diet. Among them, almonds and hazelnuts are especially notable for their high tocopherol content. For example, 100 grams of almonds provide between 24 and 26 mg of vitamin E, while hazelnuts can provide more than 21 mg for the same amount. Other nuts such as pine nuts, peanuts, pistachios, and walnuts also contain significant amounts of this nutrient, although in smaller quantities.
- Almonds : 24–26 mg/100g
- Hazelnuts : 21–26 mg/100g
- Peanuts : 8–9mg/100g
- Pistachios : 2–5 mg/100g
- Nuts : 2–9 mg/100g
The recommended daily amount of vitamin E for adults ranges from 8 to 10 mg, so a moderate serving of nuts can easily cover your daily needs.
Health benefits of tocopherol
Tocopherol offers multiple health benefits, many of which are associated with the regular consumption of nuts:
-
Antioxidant protection : Neutralizes free radicals, helping to prevent cellular aging and the development of cardiovascular diseases and some types of cancer.
-
Cardiovascular health : Nuts, rich in healthy fats and tocopherols, help reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels and maintain or increase HDL (“good”) cholesterol, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
-
Skin care : Vitamin E improves hydration, elasticity and regeneration of skin tissues, in addition to protecting the skin from solar radiation and pollution.
-
Immune system booster : Supports immune response and helps protect against infections.
-
Prevention of eye and neurological disorders : May reduce the risk of cataracts, macular degeneration, and age-related cognitive decline.
-
Red blood cell synthesis : It is involved in the formation of red blood cells and in the protection of tissues such as lungs and muscles.
Other nutrients and beneficial compounds in nuts
In addition to vitamin E, nuts provide:
-
Healthy fatty acids : Monounsaturated fatty acids predominate (such as oleic acid in almonds and hazelnuts), which are heart-healthy.
-
Polyphenols : Antioxidant compounds that enhance protection against cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer.
-
B vitamins , folic acid and vitamin K: Important for energy metabolism, brain function, bone health and blood clotting.
-
Minerals : Magnesium, potassium, calcium and iron, essential for multiple physiological functions.
How to incorporate nuts into your diet
Nuts can be eaten in a variety of ways: as a snack, in salads, yogurts, desserts, or even in main dishes. It's recommended to choose natural or roasted versions without salt or added sugar to maximize their nutritional benefits.
Conclusion
Tocopherol, or vitamin E, is a fundamental component of nuts, especially almonds and hazelnuts. Regular consumption of tocopherols, as part of a balanced diet, provides powerful antioxidant action and numerous benefits for cardiovascular health, skin, the immune system, and the prevention of chronic diseases. Including a variety of nuts in your daily diet is a simple and delicious strategy to ensure an adequate intake of this essential nutrient.





Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.