In the field of nutrition, nuts are recognized for their abundance of healthy fats, plant-based proteins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, their contribution of histidine, an essential amino acid, is less well-known and deserves special attention due to its crucial role in energy, the immune system, and overall well-being. Integrating this nutrient through nuts not only enhances daily vitality but also contributes to sustained health over time.
What is histidine and why is it essential?
Histidine is one of the twenty proteinogenic amino acids and is classified as essential, meaning it cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet. Among its main functions is being a precursor to histamine, a key substance in immune defenses, sleep regulation, and digestive functions. It also participates in hemoglobin synthesis, promoting oxygen transport and preventing fatigue. Furthermore, it contributes to cell growth, neuronal protection, and tissue regeneration. An adequate level of histidine in the diet is fundamental to maintaining multiple physiological processes in balance.
The contribution of histidine in nuts
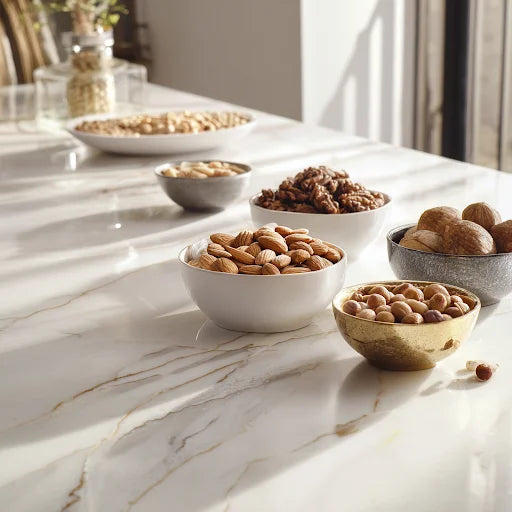
Dried fruits contain vegetable proteins that include all essential amino acids, including histidine. Some varieties are especially rich in this amino acid:
- Almonds : offer a significant proportion of protein and histidine, ideal for a robust nutritional profile.
- Walnuts and pistachios : in addition to healthy fatty acids, they provide histidine, which helps with brain function and energy.
- Cashews and peanuts : the latter, although botanically legumes, are consumed as nuts and provide an important protein and histidine content.
Consuming these foods regularly promotes the recommended daily intake of essential amino acids, optimizing numerous metabolic processes.
Histidine and energy: the relationship with daily vitality
The presence of histidine in the diet is directly related to the body's energy support. This is because:
- It is involved in the synthesis of hemoglobin, facilitating the efficient transport of oxygen to the tissues and preventing fatigue.
- When metabolized into histamine, it regulates the sleep-wake cycle, promoting recovery and physical and mental performance.
- It participates in detoxification and the maintenance of acid-base balance, processes that contribute to the optimization of energy metabolism.
Therefore, regular consumption of nuts is an effective nutritional support for those seeking stable and sustained energy throughout the day.
Additional health benefits of histidine
Beyond energy, histidine provides various benefits for the human body:
Immune system
It contributes to the production of histamine, which enhances the immune response to infections and other external aggressions.
Digestive health
Through histamine, histidine is fundamental in regulating gastric secretion and protecting the intestinal mucosa, promoting proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Neurological protection
This amino acid is involved in maintaining the myelin sheath that covers neuronal axons, improving nerve transmission, memory, and concentration.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Thanks to its antioxidant action and the regulation of lipids in the blood, histidine contributes to cardiovascular health, preventing premature aging and protecting the arteries.
Tissue repair and regeneration
It is central to the synthesis of structural proteins, facilitating tissue regeneration after injury and skin healing.
Importance for vegetarian and vegan diets
Those who choose plant-based diets require reliable sources of essential amino acids. Nuts are a practical and efficient resource for ensuring adequate levels of histidine, complementing grains and legumes and maintaining the protein balance necessary for muscle and overall health.
Recommended daily amounts
Recommended histidine intake for adults is usually around 10 mg per kilogram of body weight per day. Thus, a 70 kg person would need about 700 mg daily, an amount easily achievable through a varied diet that includes moderate portions of nuts—for example, 30 grams of almonds or cashews provide a significant portion of the daily requirement.
Tips for increasing histidine through nuts
- Add raw, unsalted nuts as a healthy snack between meals.
- Incorporate nuts, pistachios, or almonds into salads, yogurts, and desserts to improve the protein value.
- Prepare nut butters or pastes that can serve as a base for sauces, breakfasts, or energizing snacks.
- Prefer fresh and well-preserved dried fruits to avoid the formation of unwanted histamine, especially in sensitive people.
Conclusions
Histidine, abundantly present in nuts such as almonds, cashews, walnuts, and pistachios, is a key factor for energy, immunological protection, neurological balance, and disease prevention. Choosing these foods as part of a balanced diet allows access to the wide benefits of this essential amino acid and enhances vitality day by day.
Consuming nuts is much more than just enjoying a snack: it's a gesture of holistic health that supports energy and overall well-being, backed by the nutritional richness of histidine.





Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.